Introduction
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework that ensures the right individuals have appropriate access to technology resources. As businesses increasingly rely on digital solutions, IAM becomes crucial for securing sensitive data and managing user identities.
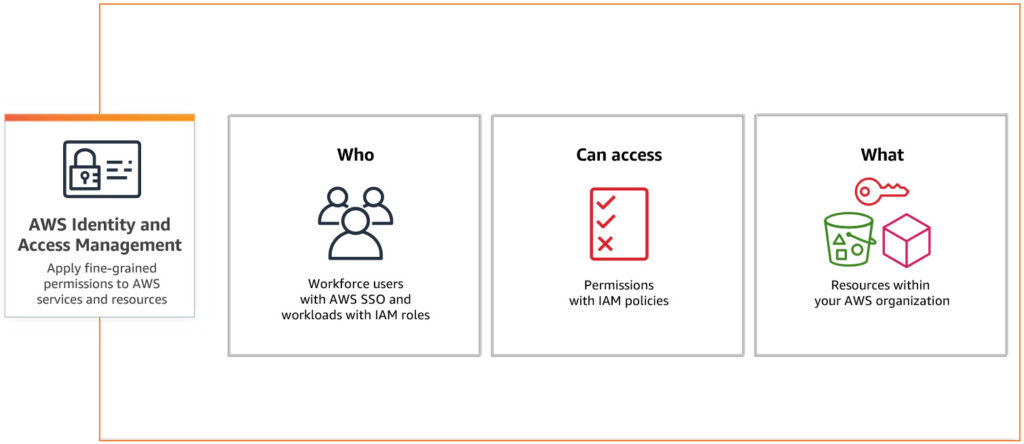
What is IAM?
IAM is a set of policies, processes, and technologies used to manage digital identities and control access to resources within an organization. It encompasses:
- User Identity Management: Creating, maintaining, and deleting user accounts.
- Access Management: Defining and enforcing policies to ensure users have the correct access levels.
- Authentication and Authorization: Ensuring users are who they claim to be and granting them permissions accordingly.
Key Components of IAM
- Identity Governance: Ensuring compliance with policies and regulations by managing the lifecycle of user identities.
- Access Control: Implementing measures like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) to manage permissions.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Allowing users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhancing security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Controlling and monitoring access for users with elevated permissions.
Benefits of IAM
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Improved User Experience: Simplifies the login process and reduces password fatigue.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations comply with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
- Operational Efficiency: Automates user provisioning and de-provisioning, saving time and reducing errors.
Challenges in Implementing IAM
- Complexity: Integrating IAM solutions with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Scalability: Ensuring the IAM solution can scale with the growth of the organization.
- User Adoption: Encouraging users to follow IAM protocols and use new systems effectively.
- Balancing Security and Usability: Ensuring robust security measures without compromising user experience.
Best Practices for IAM Implementation
- Define Clear Policies: Establish comprehensive IAM policies aligned with business goals and regulatory requirements.
- Implement Least Privilege: Ensure users only have access to the resources necessary for their roles.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct periodic audits to identify and rectify any discrepancies in access rights.
- Leverage Automation: Use automated tools for user provisioning, de-provisioning, and access reviews.
- Educate Users: Provide training and resources to help users understand and comply with IAM policies.
IAM in Cloud Environments
As organizations move to the cloud, IAM becomes even more critical. Cloud IAM solutions, like AWS IAM, Azure AD, and Google Cloud IAM, offer advanced features to manage identities and access in a cloud-native environment. These solutions provide:
- Centralized management of identities across multiple cloud services.
- Fine-grained access control to cloud resources.
- Integration with on-premises IAM systems for hybrid cloud environments.
Future Trends in IAM
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Using AI/ML to detect anomalies and predict potential security threats.
- Blockchain for Identity Management: Leveraging blockchain technology to create decentralized and tamper-proof digital identities.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Implementing a Zero Trust approach where no entity, inside or outside the network, is trusted by default.
Conclusion
IAM is a critical component of modern IT security strategies, ensuring that the right people have the right access to the right resources at the right time. By implementing robust IAM practices, organizations can protect their digital assets, comply with regulatory requirements, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
